IMPORTANT CURRENT AFFAIRS NOTES-March 2021
IMPORTANT CURRENT AFFAIRS NOTES-March 2021
3. INDIA, JAPAN SPACE AGENCIES REVIEW COOPERATION IN EARTH OBSERVATION
4. LUNAR POLAR EXPLORATION MISSION
Cannabis in the context of India
Legal Provisions in the context of India
The UN Commission on Narcotic Drugs (CND)
6. CHIEF MINISTER AND HIS COUNCIL
What is the term of Chief Minister’s office?
Chief Minister and the Governor
- Lingaraja Temple is a Hindu temple dedicated to Shiva and is one of the oldest temples in Bhubaneswar, the capital of the Indian state of
- Built by king Jajati Keshari of Soma Vansh.
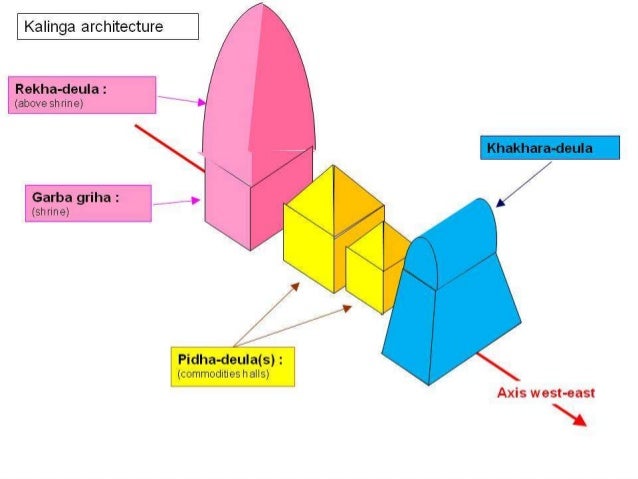
- It is built in red stone and is a classic example of Kalinga style of architecture.
- Located to the north of the temple is Bindusagar Lake.
- The temple has images of Vishnu, possibly because of the rising prominence of Jagannath sect emanating from the Ganga rulers who built the Jagannath Temple in Puri in the 12th century.
- The top leaders of India, the US, Japan and Australia will hold their first summit in a virtual format under the framework of the Quadrilateral coalition or Quad on March 12, in a major move to further expand cooperation in the Indo-Pacific amid rising global concerns over China’s growing assertiveness in the region.
- The leaders will discuss regional and global issues of shared interest, and exchange views on practical areas of cooperation towards maintaining a free, open and inclusive Indo-Pacific region.
- Prime Minister of India will be participating, along with Prime Minister of Australia Scott Morrison and Prime Minister of Japan Yoshihide Suga and President of USA Joseph R. Biden, in the first Leaders’ Summit of the Quadrilateral Framework
- The summit will provide an opportunity to exchange views on contemporary challenges such as resilient supply chains, emerging and critical technologies, maritime security, and climate change.
- In November 2017, India, Japan, the US and Australia gave shape to the long-pending proposal of setting up the Quad to develop a new strategy to keep the critical sea routes in the Indo-Pacific free of any influence.
3. INDIA, JAPAN SPACE AGENCIES REVIEW COOPERATION IN EARTH OBSERVATION
- Indian and Japanese space agencies recently reviewed cooperation in earth observation, lunar cooperation and satellite navigation, and also agreed to explore opportunities for cooperation in “space situational awareness and professional exchange programme”.
- This was agreed during a bilateral meeting between the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) and the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) held virtually.

- Both agencies signed an Implementing Arrangement for collaborative activities on rice crop area and air quality monitoring using satellite data.
- India and Japan are already working on a joint lunar polar exploration (LUPEX) mission and the two space agencies have been working on the mission that aims to send a lander and rover to the Moon’s South Pole around 2024.
- Early this month, India and Italy decided to explore opportunities in earth observation, space science and robotic and human exploration.
- Recently, India and Australia signed an amendment to the MoU which will build on the Comprehensive Strategic Partnership. Both countries are also in discussions for Australia to host vital tracking infrastructure to support the Gaganyaan manned space flight mission.
4. LUNAR POLAR EXPLORATION MISSION
- The Lunar Polar Exploration mission (LUPEX) is a robotic lunar mission concept by Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) and Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) that would send a lunar rover and lander to explore the South Pole region of the Moon in 2024.
- JAXA is likely to provide the under-development H3 launch vehicle and the rover, while ISRO would be responsible for the lander.
- The mission concept has not yet been formally proposed for funding and planning.
- In November 2019, ISRO officials stated that a new lunar lander mission was being studied for launch in November 2020; this new proposal is called Chandrayaan-3 and it would be performed by ISRO alone as a repeat attempt to demonstrate the landing capabilities needed for the Lunar Polar Exploration proposed in partnership with Japan in 2024.
- Cannabis is a generic term used to denote the several psychoactive preparations of the plant Cannabis sativa.
- The major psychoactive constituent in cannabis is Delta-9 tetrahydrocannabinol (THC).
- The Mexican name ‘marijuana‘is frequently used in referring to cannabis leaves or other crude plant material in many countries.
- Most species of cannabis are dioecious plants that can be identified as either male or female.
- The unpollinated female plants are called
- Cannabis oil (hashish oil) is a concentrate of cannabinoids obtained by solvent extraction of the crude plant material or the resin.
- Cannabis is the most widely cultivated, trafficked and abused illicit drug in the world.

- It has been found useful in cancer treatment like in multiple myeloma.
- Many people suffering from anxiety and depression are known to buy it legally in the US and bring it back to India for personal use in small quantities.
- Cannabis impairs cognitive development (capabilities of learning), including associative processes, free recall of previously learned items is often impaired when cannabis is used both during learning and recall periods.
Cannabis in the context of India:
- In India, cannabis, also known as bhang, ganja, charas or hashish, is typically eaten (bhang golis, thandai, pakoras, lassi, etc.) or smoked (chillum or cigarette).
- Ayurvedic texts refer to cannabis as a treatment for several maladies, and it is categorised as Upavisha Varga (sub poisonous), and its recreational use has been described as toxic.
- Odisha is one of the leading cannabis-producing States in India.
Legal Provisions in the context of India:
- The Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances Act, 1985 (NDPS Act) outlaws the recreational use of cannabis.
- Under the Act, the production, manufacture, possession, sale, purchase, transport, and use of cannabis is a punishable offence.
- The NDPS Act, however, does not apply to the leaves and seeds of cannabis plants.
- In case the CBD is extracted from the leaves of the cannabis, then technically it is not illegal.
- CBD oil manufactured under a license issued by the Drugs and Cosmetics Act, 1940 can be legally used.
- The Narcotics Control Bureau (NCB) is vested with the power to charge individuals in cases related to the illegal use and supply of narcotics.
- However, the use of cannabis as a medicine is not much prevalent in India.
The UN Commission on Narcotic Drugs (CND)
- The Vienna-based CND was founded in 1946.
- It is the UN agency mandated to decide on the scope of control of substances by placing them in the schedules of global drug control conventions.
- Currently, over 50 countries allow medicinal cannabis programmes, and its recreational use has been legalised in Canada, Uruguay and 15 states of the USA.
6. CHIEF MINISTER AND HIS COUNCIL
- Chief Minister’s position in state is analogous to the prime ministers position at the centre.
- The governor appoints the leader of the largest party of the house or leader chosen by the largest coalition to become the chief minister.
- The governor may exercise situational discretion if no party has clear majority. He may ask a leader to become chief minister and then prove his majority on floor of the house.
- In case the chief minister dies and no successor is present then the governor may appoint one at his discretion but if the ruling party has a nominee then the governor has no choice but to appoint that person.
- CM must become member of either house within 6 months or else he ceases to become the CM.
- CM occupies position at the governors pleasure but the governor can’t dismiss him till he has a majority in the house.
- As head of the council of ministers he recommends people to be appointed as ministers to the governor.
- He allocates and reshuffles portfolios amongst them. He can ask the minister to resign or tell the governor to dismiss him. He supervises activities of all ministers. His resignation or death leads to dissolution of the council of ministers.
- He communicates to the governor all matters related to the administration of the state and proposed legislations. He furnishes information required by the governor relating to administration of the union or proposed legislation. He submits to the consideration of the council of ministers any matter on which decision has been taken by an individual minister but the CoM hasn’t considered it.
- He can advice the governor to summon or prorogue the house sessions.
- He can advise the dissolution of the legislative assembly to the governor anytime. He announces government policies on the floor of the house.
- He is the advisor of the governor regarding appointments to various regulators and constitutional bodies of the union.
What is the term of Chief Minister’s office?
- Theoretically, the Chief Minister holds office during the pleasure of the Governor. However, in actual practice, the Chief Minister remains in the office so long as he continues to be the leader of the majority in the State Legislative Assembly. The Governor can dismiss him in case he loses his majority support.
- The CM + Council of ministers are the real executives of the state. They aid and advise the governor in the exercise of his functions but such advice is not binding on the governor. 42nd amendment didn’t make it binding on the governor as it did to the president.
- Governor has been given discretionary powers too. No court shall inquire into the advice given by the CoM to the governor. The council shall always be there to aid and advice the governor hence even if the legislative assembly is dissolved or the council has resigned still they have to continue in office till their successors are assuming charge.
- The total strength of the CM + CoM shall not exceed 15% of the strength of the legislative assembly [91st amendment]. But the number of CM + CoM shall not be less than 12. The person who has been disqualified on grounds of defection shall also be disqualified to be appointed as the CM / Minister. [91st amendment.
- The Council of Ministers is collectively responsible for the legislative assembly. A minister who isn’t a member of any house for six consecutive months shall cease to be the minister. A minister can take part in proceedings of both houses as he is a member of the government but can vote only in the house of which he’s a member.
- A member of any house disqualified on grounds of defection shall be disqualified from becoming a minister too.
- This means that the entire CoM is a team that sinks or swims together. So if the legislative assembly passes a no-confidence motion against the CoM then all have to resign. Only the legislative assembly can pass the motion of no confidence; it can’t be against a single minister but the entire CoM only.
- This is due to the provision in the constitution saying:
- “Council of Ministers is collectively responsible to the legislative assembly.”

Chief Minister and the Governor
- The relationship between the Chief Minister of the state and the state’s governor has always been in the news. The debate on the authority of the respective posts has made the rounds throughout
- Article 163: The governor is advised by the council of ministers which is headed by the Chief Minister.
Note: When the governor acts at his own discretion, no advice is needed by the council
- Article 164: Governor appoints Chief Minister and later Chief Minister recommends Governor on the appointment of ministers
- Article 167: Chief Minister has to communicate all administrative decisions that are taken up by him and the council of ministers to the governor
There are three categories of ministers in the council:
- Cabinet: They attend cabinet meetings and play important role in state government.
- Minister of state: They can be independent in charge of departments that aren’t attached to cabinet ministries or in charge of a specific departments part of a ministry /specific work in a ministry which is headed by a cabinet minister.
- Deputy Minister: They are attached to cabinet ministers or ministers of state and assist them in their work.
Arise, awake, and,
stop not till the goal is reached.
Swami Vivekananda
Click here for Daily Current Affairs Quiz
Click here for Daily Current Affairs Notes

